Dynamic programming to identify contiguous subarray with maximum sum
In Computer Science, the maximum sum subarray problem is the task of finding a contiguous subarray with the largest sum, within a given one-dimensional array of integer numbers - each number in the input array could be positive, negative, or zero.
Let’s write a O(n) function in Python to find both the contiguous subarray with the largest sum and its sum given an input array of integers.
This well-known problem can be solved via different algorithmic techniques, including brute force, divide and conquer, reduction to shortest paths, and dynamic programming. Here I am going to implement a solution using dynamic programming. Also, please note that it is not possible to directly apply the Kadane’s algorithm because we not only need to get its sum, but we also need to return the subarray itself.
Question
The task is to write a function that takes in an input array of integer numbers and returns both the contiguous subarray that has the largest sum and the corresponding sum. Also, the requirement is for the function to have a linear time complexity.
Examples
Please refer to the table below as per some examples of input arrays and the corresponding expected function outputs.
| input | output |
|---|---|
| [-2, 5], | ([5], 5) |
| [1, -3, 7, 0, -5, 9, -3], | ([7, 0, -5, 9], 11) |
| [0], | ([0], 0) |
| [-8, 0, 0, 0, 0, -2], | ([0], 0) |
| [8, 10, -6, -4, -7, 2], | ([8, 10], 18) |
| [-8, -4, -7, -2, 2, 7], | ([2, 7], 9) |
| [-4, 1, -10, 7, 9, 4], | ([7, 9, 4], 20) |
| [-3, 10, 2, -10, 3, -9], | ([10, 2], 12) |
| [10, 3, 8, -1, -2, 7], | ([10, 3, 8, -1, -2, 7], 25) |
| [5, 4, -7, -4, -1, 2], | ([5, 4], 9) |
| [10, 9, -9, -1, 3, 7], | ([10, 9], 19) |
| [-9, -4, 4, 0, 9, 10], | ([4, 0, 9, 10], 23) |
| [7, 2, -8, 1, -3, 10], | ([10], 10) |
| [4, 4, -5, -8, 8, 2], | ([8, 2], 10) |
| [-2, -3, -5, -7, -1], | ([-1], -1) |
| [-2, -3, -1, -5, -7], | ([-1], -1) |
Hint: in looping through the input array’s elements, make use of a index to track when the current element is greater than the current sum up to the same element!
Lay out your structure
I am going to implement the following approach:
- start by initializing:
- both the maximum sum (
global_max) and the current sum (current_max) equal to the first element of the array - the starting index (
start), the ending index (end), and the index with which to track the start of the potential largest subarray (index_potential_maximum_subarray_starts) equal to 0
- both the maximum sum (
- loop through the input array, starting from the second element, and perform the following checks:
- if the current element is greater than the current sum plus the current element, then assign the current sum equal to the current element and store the current index for the start of the potential largest subarray; otherwise, update the current sum by adding the current element to it
- if the resulting current sum is greater than the maximum sum recorded so far, then assign the maximum sum equal to the current sum and assign the start index equal to the index previously recorded as the starting index of the potential largest sum, and the end index equal to the current index
At the end of the above process I am going to return the contiguous subarray with the largest sum (by slicing the input array from the start index up to the end index plus 1), along with its sum.
Step 1: write the function
Now we are ready to write our function following the instructions discussed above - I bet you will get a much better understanding of the process by reading the code! :)
def find_contiguous_subarray_max_sum(array: "list of ints") -> ("list of ints", int):
"""Return the contiguous sub-array with the greatest sum within an input array, together with its sum.
Args:
array (list): a non-empty list of integer numbers.
Returns:
(list, int): a tuple consisting of the contiguous sub-array with the maximum sum and its sum.
Raises:
TypeError: If the input array is not a list.
ValueError: If the input array is either an empty list or a list not containing integer numbers only.
Notes:
Time complexity is O(n) as we loop over every element of the input array only once.
Space complexity is O(n) as we store a sub-array whose maximum length is the length of the array;
also, we instantiate variables with single values.
Examples:
>>> array = [-2, 5]
>>> find_contiguous_subarray_max_sum(array)
([5], 5)
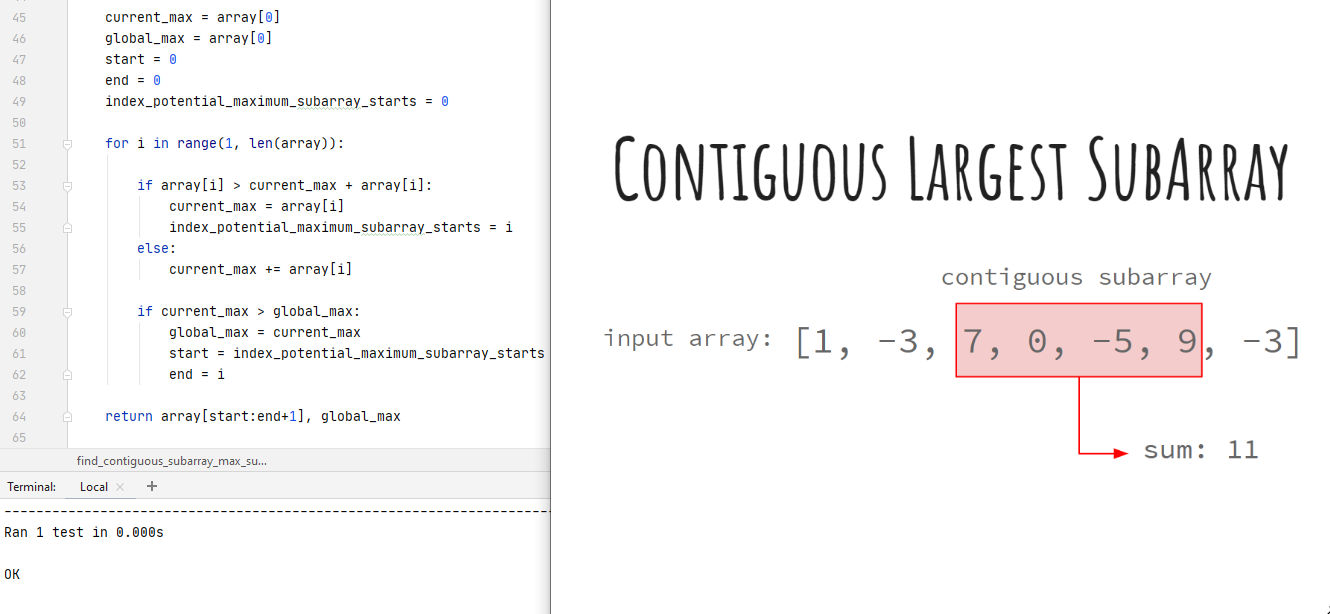
>>> array = [1, -3, 7, 0, -5, 9, -3]
>>> find_contiguous_subarray_max_sum(array)
([7, 0, -5, 9], 11)
"""
if not isinstance(array, list):
raise TypeError("'array' must be a list.")
if not (len(array) > 0 and all(isinstance(x, int) for x in array)):
raise ValueError("'array' must be a non-empty list of integers only.")
current_max = array[0]
global_max = array[0]
start = 0
end = 0
index_potential_maximum_subarray_starts = 0
for i in range(1, len(array)):
if array[i] > current_max + array[i]:
current_max = array[i]
index_potential_maximum_subarray_starts = i
else:
current_max += array[i]
if current_max > global_max:
global_max = current_max
start = index_potential_maximum_subarray_starts
end = i
return array[start:end+1], global_max
Step 2: run the tests
Let’s check if the function works as expected.
We can perform the automatic check of all input arrays contained in a list and verify the expected result. To this purpose, we can build a unit test. Here is the code for it.
import unittest
import contiguous_subarray_maximum_sum as csms
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
class TestLargestSubarray(unittest.TestCase):
arrays = [
[-2, 5],
[1, -3, 7, 0, -5, 9, -3],
[0],
[-8, 0, 0, 0, 0, -2],
[8, 10, -6, -4, -7, 2],
[-8, -4, -7, -2, 2, 7],
[-4, 1, -10, 7, 9, 4],
[-3, 10, 2, -10, 3, -9],
[10, 3, 8, -1, -2, 7],
[5, 4, -7, -4, -1, 2],
[10, 9, -9, -1, 3, 7],
[-9, -4, 4, 0, 9, 10],
[7, 2, -8, 1, -3, 10],
[4, 4, -5, -8, 8, 2],
[-2, -3, -5, -7, -1],
[-2, -3, -1, -5, -7],
]
subarray_expected_result = [
([5], 5),
([7, 0, -5, 9], 11),
([0], 0),
([0], 0),
([8, 10], 18),
([2, 7], 9),
([7, 9, 4], 20),
([10, 2], 12),
([10, 3, 8, -1, -2, 7], 25),
([5, 4], 9),
([10, 9], 19),
([4, 0, 9, 10], 23),
([10], 10),
([8, 2], 10),
([-1], -1),
([-1], -1),
]
def test_find_contiguous_subarray_max_sum(self):
for s, r in zip(self.arrays, self.subarray_expected_result):
result = csms.find_contiguous_subarray_max_sum(s)
self.assertEqual(result, r)
And we can run the test from the terminal with the following command.
$ python test_contiguous_subarray_maximum_sum.py
The test result is positive as shown below.
.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 1 test in 0.000s
OK
Conclusions
I hope you found this post useful - I would love to hear from you what you think about my Python script.
What do you think about my function?
Also, please share with me one coding challenge you had to face recently! :)
~Giuseppe