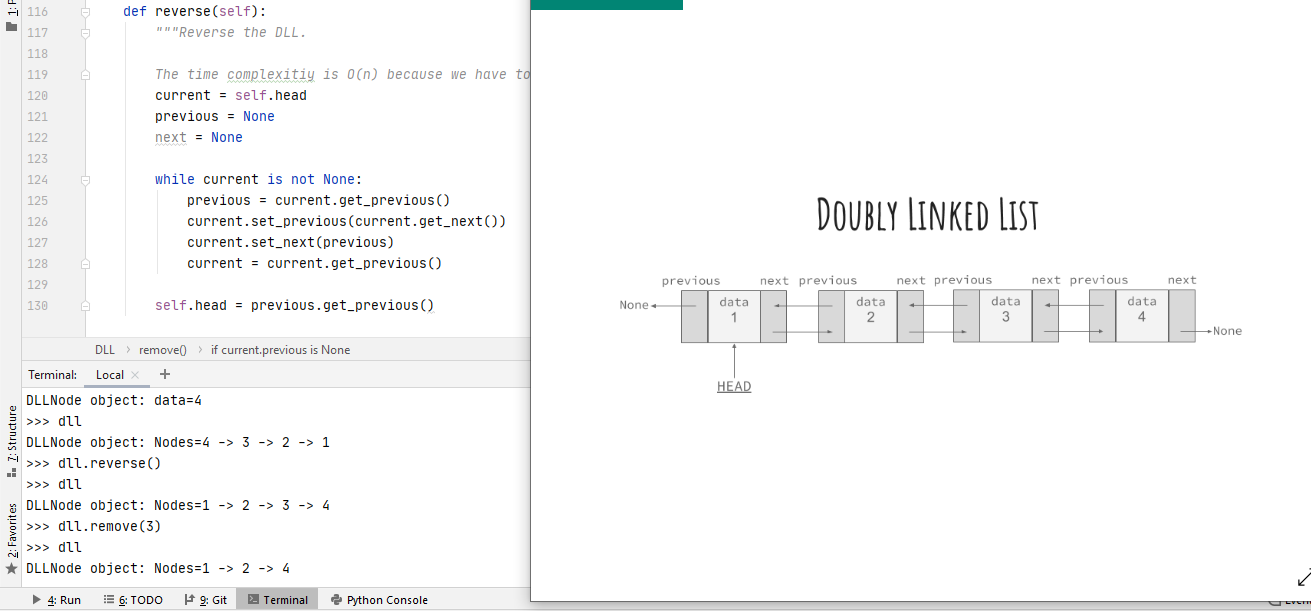
In-place reversal of a Doubly Linked List in linear time
“Write me a function that performs an in-place reversal of a Doubly Linked List in linear time.”
This is one of the most common interview questions you might face about the implementation of Abstract Data Types.
I am going to assume that you are familiar with the underlying ideas of Doubly Linked Lists, otherwise I hope you will get a good understanding of it by reading my code! :)
Question
The task is to write a function to reverse a Doubly Linked List in-place and in linear time.
To this purpose, we first need to implement a Doubly Linked List.
Example
For example, suppose we have a Doubly Linked List made of the following Nodes:
“4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1”.
As a result of calling the reverse() method on the Doubly Linked List, it would look like the following:
“1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4”.
Hint: in looping through the Nodes make sure to keep track of the last Node so that you can re-assign the Doubly Linked List’s Head to it!
Lay out your structure
I am going to implement the following approach:
- Implement a class for a Node of a Doubly Linked List (
DLLNode) - Implement a class for the Doubly Linked List (
DLL) - Write a method to reverse the Doubly Linked List in-place and in linear time (
reverse()).
Step 1: write the DLLNode class
Now we are ready to implement the Node of the Doubly Linked List.
class DLLNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.previous = None
def __repr__(self):
return "DLLNode object: data={}".format(self.data)
def get_data(self):
return self.data
def set_data(self, new_data):
self.data = new_data
def get_next(self):
return self.next
def set_next(self, new_next):
self.next = new_next
def get_previous(self):
return self.previous
def set_previous(self, new_previous):
self.previous = new_previous
Step 2: write the DLL class
Next, we need to implement the data structure for the Doubly Linked List.
class DLL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.size = 0
def __repr__(self):
"""Return a string representation of the DLL.
The time complexity is O(n) as we need to loop through the entire DLL.
"""
nodes = []
current = self.head
while current:
nodes.append(str(current.get_data()))
current = current.get_next()
return "DLLNode object: Nodes={}".format(' -> '.join(nodes))
def is_empty(self):
"""Return True or False whether the DLL is empty, respectively.
The time complexity is O(1) as we evaluate an equality."""
return self.head is None
def size(self):
"""Return the size of the DLL.
The time complexity is O(1) as we return a parameter."""
return self.size
def search(self, data):
"""Traverse the DLL and return True or False whether or not the data is present in one of the Nodes.
The time complexity is O(n) because in the worst case we must visit all Nodes in the DLL.
"""
if self.head is None:
return "The Doubly Linked List is empty - there is no node to search."
current = self.head
while current is not None:
if current.get_data() == data:
return True
else:
current = current.get_next()
return False
def add_front(self, data):
"""Add a Node with the data argument to the front of the DLL.
The time complexity is O(1) as we only perform a few assignments."""
temp = DLLNode(data)
temp.set_next(self.head)
if self.head is not None:
self.head.set_previous(temp)
self.head = temp
self.size += 1
def remove(self, data):
"""Remove the first occurrence of a Node containing the data argument as its data attribute.
The time complexity is O(n) because in the worst case we must visit all Nodes in the DLL
before finding the one we want to remove.
"""
if self.head is None:
return "The Doubly Linked List is empty - there is no node to remove."
current = self.head
found = False
while not found:
if current.get_data() == data:
found = True
else:
if current.get_next() is None:
return "The Doubly Linked List has no Node with {} value.".format(data)
else:
current = current.get_next()
if current.previous is None:
self.head = current.get_next()
else:
current.previous.set_next(current.get_next())
current.next.set_previous(current.get_previous())
As you can see, I have added the most common methods of the Doubly Linked Lists, namely is_empty(), size(), search(), add_front(), and remove().
Step 3: write the reverse() method
Finally, we can write the Doubly Linked List’s function to reverse it in-place and in linear time.
def reverse(self):
"""Reverse the DLL.
The time complexitiy is O(n) because we have to visit all Nodes in the DLL."""
current = self.head
previous = None
next = None
while current is not None:
previous = current.get_previous()
next = current.get_next()
current.set_previous(next)
current.set_next(previous)
current = current.get_previous()
self.head = previous.get_previous()
Of course, the above piece of code has to be included within the DLL class.
Basically, I start by initializing three variables: current, previous, and next. The idea is to loop through all the Nodes by pointing at each of them via the current variable and, first of all, store their next and previous into next and previous, respectively. Then, we swap the current’s previous and next Nodes with each other.
One important note. Once we get to the last Node of the Doubly Linked List, we assign its previous Node to the previous variable. Then, when the current variable becomes None (that is the now previous element of the last Node), we can re-assign the Head of the Doubly Linked List to take the previous’ previous Node (that is the last Node of the Doubly Linked List).
Test the function
We can test the revere() function from the terminal.
Let’s run the script in interactive mode with the following command.
python -i reverse_doubly_linked_list.py
And now let’s test the code.
>>> dll = DLL()
>>> dll.is_empty()
True
>>> dll.add_front(1)
>>> dll.is_empty()
False
>>> dll.add_front(2)
>>> dll.add_front(3)
>>> dll.add_front(4)
>>> dll.search(2)
True
>>> dll.size
4
>>> dll.head
DLLNode object: data=4
>>> dll
DLLNode object: Nodes=4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
>>> dll.remove(3)
>>> dll
DLLNode object: Nodes=4 -> 2 -> 1
>>> dll.reverse()
>>> dll
DLLNode object: Nodes=1 -> 2 -> 4
All methods of the DLL class work as expected. Nicely done!
If you have doubts about how the while look works, I would suggest to run it from the command line and add a print statement like the following, so that at each current Node you get a clear picture of what Node each variable is pointing at.
print("previous:{}, current:{}, next:{}".format(previous, current, next))
Conclusions
I hope you found this post useful - I would love to hear from you what you think about my Python script.
What do you think about my function?
Also, please share with me one coding challenge you had to face recently! :)
~Giuseppe