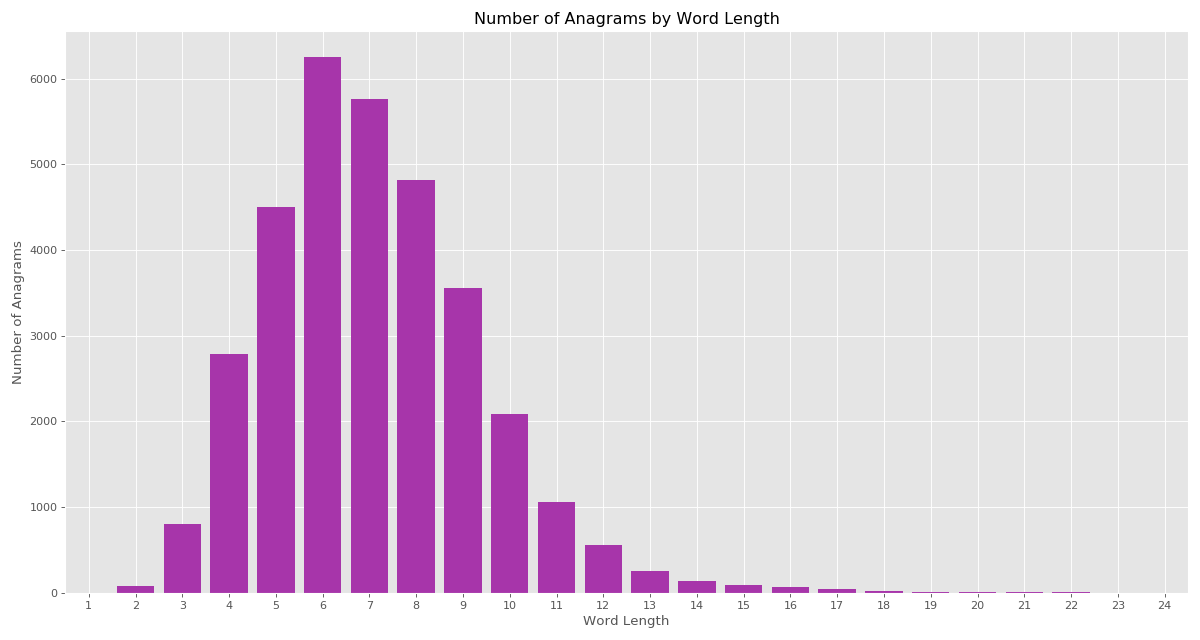
Find the number of anagrams by words length
Let’s build an anagram finder together. An anagram is a word (or phrase) formed by rearranging the letters of a word (or phrase), typically using all the original letters exactly once.
Question
Given a list of words in a file, group the words by their length and find the total number of anagrams within each group, meaning for each length.
Please disregard the trivial anagrams, meaning all words who are the only anagram of themselves (in other words, only consider the words that have 2 or more anagrams).
Note: We expect to find very few anagrams for long words, whereas there are more anagrams for short words.
Example of input and final output
Here you can find an example of the input file, a list of words.
['abbasi',
'abbassi',
'abbasside',
'abbatial',
'abbatical',
'abbess',
'abbey',
'abbeystede',
'abbie',
'abbot',
'abbotcy']
Here you can find the final output.
{1: 0,
2: 80,
3: 805,
4: 2790,
5: 4497,
6: 6246,
7: 5759,
8: 4821,
9: 3552,
10: 2082,
11: 1054,
12: 558,
13: 250,
14: 140,
15: 90,
16: 70,
17: 44,
18: 20,
19: 14,
20: 6,
21: 8,
22: 4,
23: 0,
24: 0}
Lay out your structure
Here is the structure we will follow to solve this little exercise:
- group words by their length
- find all anagrams in each group
- count the total number of unique anagrams in each group
Load the data
Let’s load the data by running the following code.
# from a given file, create a sorted list of unique lower-case words with no '\n' character
wordclean = sorted(list(set([word.strip().lower() for word in open('words', 'r').readlines()])))
print("we have a total number of words equal to: {:,}".format(len(wordclean)))
>>>"we have a total number of words equal to: 234,371"
Step 1: group words by their length
Fist of all, we need to create a dictionary of lists of words indexed by the length of words within each list.
In particular, the dictionary must be a collections defaultdictionary with a list as default, because this is the only way with which we can initialize an empty list as values in a dictionary - when a word length is added as key for the first time and the word itself is appended to the value (the list of words of same length), that same list would not yet exist and this would result in an error.
import collections
dict_of_words_list_by_length = collections.defaultdict(list)
# go through the list of words, use the length of each word to access the dictionary
# and append the word at the list of words with the same length
for word in wordclean:
dict_of_words_list_by_length[len(word)].append(word)
Let’s print some elements of this dictionary.
print(dict_of_words_list_by_length)
defaultdict(list,
{1: ['a',
'b',
'c',
'd',
'e',
'f',
'g',
'h',
'i',
'j',
'k',
'l',
'm',
'n',
'o',
'p',
'q',
'r',
's',
't',
'u',
'v',
'w',
'x',
'y',
'z'],
2: ['aa',
'ab',
'ad',
'ae',
'ah',
'ai',
...]
...
}
)
To give a better understanding of this dictionary, let’s print the words of length equal to 21.
print(dict_of_words_list_by_length[21])
['acetylphenylhydrazine',
'aminoacetophenetidine',
'anatomicopathological',
'anemometrographically',
'anthropoclimatologist',
'anthropomorphological',
'anticonstitutionalist',
'appendorontgenography',
'benzalphenylhydrazone',
'chemicopharmaceutical',
'chlamydobacteriaceous',
'cholecystogastrostomy',
'cholecystojejunostomy',
'cholecystolithotripsy',
'cholecystonephrostomy',
'choledochoenterostomy',
'choledocholithotripsy',
'chromophotolithograph',
'constitutionalization',
'counterinterpretation',
'counterpronunciamento',
'counterreconnaissance',
'cryptocrystallization',
'crystalloluminescence',
'dacryocystorhinostomy',
'deintellectualization',
'disestablishmentarian',
'disproportionableness',
'duodenocholedochotomy',
'duodenopancreatectomy',
'electroencephalograph',
'enterocholecystostomy',
'establishmentarianism',
'gastroenterocolostomy',
'glossolabiopharyngeal',
'heterotransplantation',
'hexachlorocyclohexane',
'historicogeographical',
'historicophilosophica',
'hypsidolichocephalism',
'indistinguishableness',
'intellectualistically',
'intertransformability',
'labioglossopharyngeal',
'mandibulosuspensorial',
'mechanicointellectual',
'membranocartilaginous',
'microcolorimetrically',
'microseismometrograph',
'noninterchangeability',
'otorhinolaryngologist',
'overindustrialization',
'palaeodendrologically',
'pancreatoduodenectomy',
'pathologicoanatomical',
'pentamethylenediamine',
'pharmacoendocrinology',
'pharyngoepiglottidean',
'philosophicoreligious',
'phoneticohieroglyphic',
'photochromolithograph',
'platydolichocephalous',
'poliencephalomyelitis',
'poluphloisboiotatotic',
'prostatovesiculectomy',
'protransubstantiation',
'pseudoanthropological',
'pseudohermaphroditism',
'pseudolamellibranchia',
'pseudoparthenogenesis',
'psychophysiologically',
'scientificohistorical',
'scleroticochoroiditis',
'stereophotomicrograph',
'stereoroentgenography',
'superincomprehensible',
'tessarescaedecahedron',
'thermophosphorescence',
'transubstantiationite',
'undistinguishableness',
'ureteropyelonephritis',
'zygomaticoauricularis']
Step 2: find all anagrams in each group
Now we need to create a dictionary of anagrams of words that belong to the same group, meaning all anagrams of words that have the same length.
To this purpose, we first need to define a way for retrieving all anagrams of a word.
The most efficient way to do so is to:
- define a function to get the signature of any given word
- create a dictionary of lists of anagrams indexed by their signature
- define a function to get the list of anagrams of any given word
- find all anagrams in each group
Step 2.1: define a function to get the signature of any given word
Let’s define a function to covert a word into its so-called ‘signature’, which consists of the join of its letters sorted in alphabetical order.
def signature(word):
return ''.join(sorted(word))
print("the signature of the word 'giuseppe' is: {}".format(signature('giuseppe')))
print("which is equal to the signature of the word 'seppegiu': {}".format(signature('giuseppe') == signature('seppegiu')))
>>>"the signature of the word 'giuseppe' is: eegippsu"
>>>"which is equal to the signature of the word 'seppegiu': True"
Step 2.2: create a dictionary of lists of anagrams indexed by their signature
Next, we need to create a Python dictionary of lists of all the anagrams of the words - these lists must be indexed by the shared signature of all anagrams.
In this way, getting an anagram for any given word would be as simple as looking up the dictionary for the word signature, because every item in the dictionary will have a signature as the key and a list of all words with that same signature.
In particular, as we did in Step 1, the dictionary must be a collections defaultdictionary with a list as default, because this is the only way with which we can initialize an empty list as values in a dictionary - when a word signature is added as key for the first time and the word itself is appended to the value (the list of words with the same signature, meaning all its anagrams), that same list would not yet exist and this would result in an error.
import collections
dict_of_word_list_by_signature = collections.defaultdict(list)
# go through the list of words, use the signature of each word to access the dictionary key
# and append the word at the list of anagrams, i.e. all words in the list that have the same signature
for word in wordclean:
dict_of_word_list_by_signature[signature(word)].append(word)
For example, we can print the anagrams of the word ‘are’.
print("the anagrams of the word 'are' are: {}".format(dict_of_word_list_by_signature[signature('are')]))
>>>"the anagrams of the word 'are' are: ['aer', 'are', 'ear', 'era', 'rea']"
Step 2.3: define a function to get the list of anagrams of any given word
Here is our “look up” function to efficiently retrieve the anagrams of any word from the dictionary.
def get_word_anagrams(word):
return dict_of_word_list_by_signature[signature(word)]
For example, using a dictionary comprehension, we can create a dictionary containing the list of all anagrams of each given word, disregarding the words that are the only anagram of themselves (i.e. the list of their anagram has length equal to 1) such as the word ‘account’.
dict_word_anagrams = {word: get_word_anagrams(word) \
for word in wordclean \
if len(get_word_anagrams(word)) > 1}
print("the total number of anagrams of words with non-singular anagrams is: {:,}".format(len(dict_word_anagrams)))
>>>"the total number of anagrams of words with non-singular anagrams is: 32,890"
Actually, this is the total number of anagrams of words with non-singular anagrams: 32,890. We will use this value to double check our final solution!
Step 2.4: find all anagrams in each class
Finally, we can create a dictionary of dictionaries indexed by word length, where each dictionary is the lists of anagrams indexed by the word being anagrammed, disregarding the words that are the only anagram of themselves (i.e. the list of their anagram has length equal to 1) such as the word ‘account’.
dict_of_anagrams_list_by_length = {}
for length, words in dict_of_words_list_by_length.items():
dict_of_anagrams_list_by_length[length] = {word: get_word_anagrams(word) for word in words \
if len(get_word_anagrams(word)) > 1}
Let’s print some elements of this dictionary.
print(dict_of_anagrams_list_by_length)
{1: {},
2: {'ab': ['ab', 'ba'],
'ad': ['ad', 'da'],
'ae': ['ae', 'ea'],
'ah': ['ah', 'ha'],
'ak': ['ak', 'ka'],
'al': ['al', 'la'],
'am': ['am', 'ma'],
'an': ['an', 'na'],
'ar': ['ar', 'ra'],
'as': ['as', 'sa'],
'at': ['at', 'ta'],
'aw': ['aw', 'wa'],
'ay': ['ay', 'ya'],
'ba': ['ab', 'ba'],
'da': ['ad', 'da'],
'de': ['de', 'ed'],
'di': ['di', 'id'],
'do': ['do', 'od'],
'ea': ['ae', 'ea'],
'ed': ['de', 'ed'],
'eh': ['eh', 'he'],
'em': ['em', 'me'],
'en': ['en', 'ne'],
'er': ['er', 're'],
'es': ['es', 'se'],
'ey': ['ey', 'ye'],
'fi': ['fi', 'if'],
'fo': ['fo', 'of'],
'go': ['go', 'og'],
'ha': ['ah', 'ha'],
'he': ['eh', 'he'],
'ho': ['ho', 'oh'],
'id': ['di', 'id'],
'if': ['fi', 'if'],
'in': ['in', 'ni'],
'is': ['is', 'si'],
'it': ['it', 'ti'],
'ka': ['ak', 'ka'],
'ko': ['ko', 'ok'],
'la': ['al', 'la'],
'ma': ['am', 'ma'],
'me': ['em', 'me'],
'mo': ['mo', 'om'],
'mu': ['mu', 'um'],
'my': ['my', 'ym'],
'na': ['an', 'na'],
'ne': ['en', 'ne'],
'ni': ['in', 'ni'],
'no': ['no', 'on'],
'nu': ['nu', 'un'],
'od': ['do', 'od'],
'of': ['fo', 'of'],
'og': ['go', 'og'],
'oh': ['ho', 'oh'],
'ok': ['ko', 'ok'],
'om': ['mo', 'om'],
'on': ['no', 'on'],
'or': ['or', 'ro'],
'os': ['os', 'so'],
'ow': ['ow', 'wo'],
'pu': ['pu', 'up'],
'ra': ['ar', 'ra'],
're': ['er', 're'],
'ro': ['or', 'ro'],
'sa': ['as', 'sa'],
'se': ['es', 'se'],
'si': ['is', 'si'],
'so': ['os', 'so'],
'ta': ['at', 'ta'],
'ti': ['it', 'ti'],
'tu': ['tu', 'ut'],
'um': ['mu', 'um'],
'un': ['nu', 'un'],
'up': ['pu', 'up'],
'ut': ['tu', 'ut'],
'wa': ['aw', 'wa'],
'wo': ['ow', 'wo'],
'ya': ['ay', 'ya'],
'ye': ['ey', 'ye'],
'ym': ['my', 'ym']},
3: {'aal': ['aal', 'ala'],
'aam': ['aam', 'ama'],
'aba': ['aba', 'baa'],
...
}
...
}
As expected, for each word length, we have a dictionary of lists of anagrams indexed by the word being anagrammed (please note that we got an empty dictionary for word length equal to 1).
In particular, we note that the number of keys of each dictionary is the total number of anagrams of each group!
For example, the total number of anagrams of words whose length is equal to 21 is 8.
# print the dictionary for words length equal to 21
dict_of_anagrams_list_by_length[21]
{'anatomicopathological': ['anatomicopathological', 'pathologicoanatomical'],
'chromophotolithograph': ['chromophotolithograph', 'photochromolithograph'],
'duodenopancreatectomy': ['duodenopancreatectomy', 'pancreatoduodenectomy'],
'glossolabiopharyngeal': ['glossolabiopharyngeal', 'labioglossopharyngeal'],
'labioglossopharyngeal': ['glossolabiopharyngeal', 'labioglossopharyngeal'],
'pancreatoduodenectomy': ['duodenopancreatectomy', 'pancreatoduodenectomy'],
'pathologicoanatomical': ['anatomicopathological', 'pathologicoanatomical'],
'photochromolithograph': ['chromophotolithograph', 'photochromolithograph']}
Step 3: count the total number of unique anagrams in each class
We want to know the total number of anagrams by word length.
Given this dictionary of dictionaries indexed by word length, we can get the total number of anagrams by word length by simply counting the keys of every dictionary!
dict_of_sum_anagrams_count_by_length = {}
for length, words in dict_of_words_list_by_length.items():
dict_of_sum_anagrams_count_by_length[length] = len(dict_of_anagrams_list_by_length[length].keys())
Here is the output! :)
dict_of_sum_anagrams_count_by_length
{1: 0,
2: 80,
3: 805,
4: 2790,
5: 4497,
6: 6246,
7: 5759,
8: 4821,
9: 3552,
10: 2082,
11: 1054,
12: 558,
13: 250,
14: 140,
15: 90,
16: 70,
17: 44,
18: 20,
19: 14,
20: 6,
21: 8,
22: 4,
23: 0,
24: 0}
Double Check the Solution
In order to double check our solution, we can sum the count of anagram in each group as follows.
total_number_of_anagrams = 0
for value in dict_of_sum_anagrams_count_by_length.values():
total_number_of_anagrams += value
print("the sum of the total number of anagrams by word length is: {:,}".format(total_number_of_anagrams))
>>>"the sum of the total number of anagrams by word length is: 32,890"
This number (32,890) is the same result we got before when we calculated the total number of anagrams of words with non-singular anagrams!
Bonus: Graph
As an extra step, we can visually represent the distribution of anagrams by word length.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
plt.style.use('ggplot')
# let's build a dataframe first
data = {'word_length':list(dict_of_sum_anagrams_count_by_length.keys()),
'n_anagrams':list(dict_of_sum_anagrams_count_by_length.values())}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# let's plot the data
ax = sns.barplot(data=df,
x='word_length',
y='n_anagrams',
color='#ba22bd')
ax.set(xlabel='Word Length',
ylabel='Number of Anagrams',
title='Number of Anagrams by Word Length'
)
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("find-number-of-anagrams-by-words-length.png")
plt.show()
The result will look like the image on top of this post.
Conclusions
I hope you found this post useful - I would love to hear from you what you think about my python script.
Did you manage to find an alternative, perhaps more efficient, solution?
Also, please share with me one coding challenge you had to face recently during your work! :)
~Giuseppe